In a world where sustainable farming practices are becoming increasingly crucial; aquaponics has emerged as a beacon of innovation. This symbiotic system integrates aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (soil-less plant cultivation) to create a closed relationship and eco-friendly method of growing food. As we delve into the depths of aquaponics, we’ll explore its definition, types, and the fascinating circle that fuels its productivity, and weigh its advantages against its disadvantages.
Definition of Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a sustainable agricultural system that combines aquaculture and hydroponics, creating a mutually beneficial environment for both fish and plants. In this system, fish waste provides essential nutrients for plant growth, while the plants naturally filter and purify the water for the fish. It’s a closed relationship ecosystem that copies the balance found in natural ecosystems, fostering efficient and environmentally friendly food production.
Types of Aquaponics
Aquaponic systems come in various types, each catering to different scales and preferences. Your space, resource availability, and reason for growing are some of the factors that influence your choice of the type of aquaponics to go for.
1. Media-Based Aquaponics
– Utilizes a media-filled bed where plants grow, and the media (such as gravel or clay pebbles) provides surface area for beneficial bacteria to survive in.
– Water from the fish tank is pumped into the grow beds, and the plants extract nutrients before the filtered water returns to the fish tank
Advantages
– Biofiltration: The media bed serves as a biofilter, fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria that break down ammonia into plant-friendly nutrients.
– Suitable for Various Plants: This method accommodates a wide range of plant types, including larger fruiting plants.
– Ease of Maintenance: Media-based systems are relatively easy to maintain and are suitable for beginners.
Disadvantages
– Clogging Concerns: Over time, the media may become clogged with wastes, potentially affecting the system’s efficiency.
– Limited Oxygen to Roots: Oxygen levels to plant roots may vary, potentially impacting plant health and growth
– Initial Cost: Setting up media-filled beds can incur initial costs for purchasing media and establishing the beds.
2. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
– Involves a thin film of nutrient-rich water flowing over the plant roots, providing essential nutrients while allowing the roots access to oxygen.
– Often used for smaller plants like herbs, cabbage, and lettuce.
Advantages
– Water Efficiency: NFT systems use water efficiently as they provide a constant flow of nutrients directly to the roots.
– Suitable for Leafy Greens: Ideal for growing leafy greens and herbs that grow in shallow nutrient solutions.
– Space-Efficient: NFT systems are well-suited for vertical farming and limited space situations.
Disadvantages
– Risk of Drying Out: Interruptions in the nutrient flow, due to power outages or pump failures, can lead to plants drying out quickly.
– Not Ideal for Larger Plants: NFT systems may not provide sufficient support for larger, heavier fruiting plants.
– Technical Expertise Needed: Requires a good understanding of nutrient flow dynamics, which may pose challenges for beginners.
3. Deep Water Culture (DWC)
– Plants are suspended in floating rafts above a fish tank with their roots submerged in nutrient-rich water from the fish waste
– An air stone or diffuser ensures oxygenation for both fish and plants.
Advantages
– Effective Oxygenation: DWC ensures excellent oxygenation of plant roots, promoting healthy growth.
– Ideal for Leafy Greens: Well-suited for growing leafy greens and herbs, especially those with smaller root systems.
– relatively cheaper cost because there is no need to use pumps and electricity.
– Simplicity of Design: DWC systems are relatively simple in design, making them suitable for beginners.
Disadvantages
– Limited for Larger Plants: This may not provide adequate support for larger fruiting plants with extensive root systems.
– Risk of Algae Growth: Exposed water surfaces may encourage algae growth, requiring additional maintenance.
– Potential Fish Stress: Fish may experience stress if the system is not adequately oxygenated.

4. Vertical Aquaponics
– Utilizes vertical space efficiently, allowing for increased production in limited areas.
– Stacks grow beds or towers to maximize plant growth.
– This becomes so useful for places of limited space. The vertical maximizes space for production
Advantages
– Space Utilization: Maximizes vertical space, enabling higher crop yields in limited areas.
– Aesthetically Pleasing: Vertical aquaponics systems can be visually appealing and space-saving.
– Ideal for Urban Farming: Well-suited for urban environments where space is a limited
Disadvantages
– Complex Design: Building and maintaining vertical systems can be more complex than traditional horizontal setups.
– Uneven Water Distribution: Ensuring even water distribution to all plants in a vertical setup requires careful planning.
– Initial Cost: The initial cost of setting up vertical structures may be higher than other types of aquaponics.
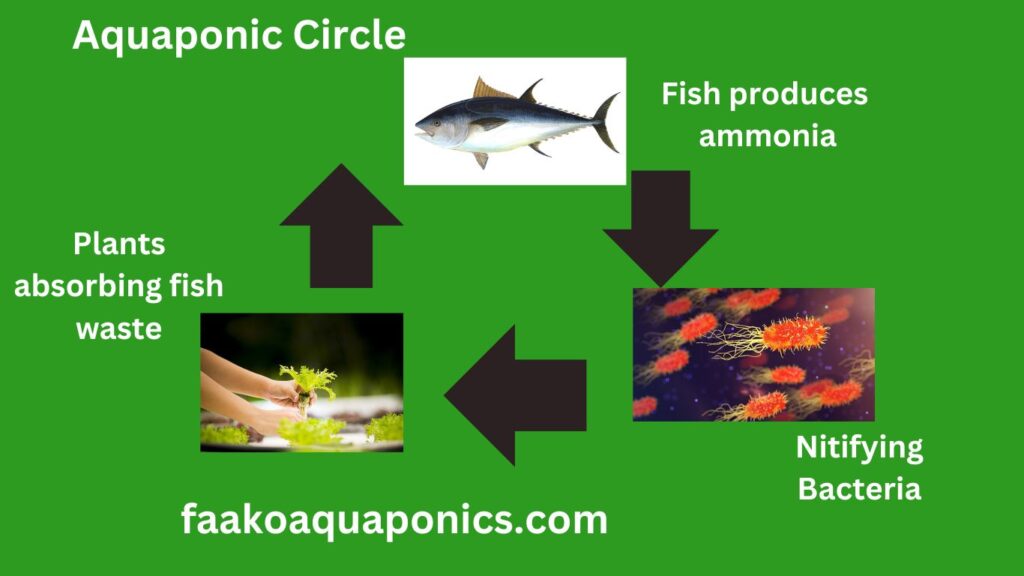
The Aquaponics Circle: How Does Aquaponics Work?
The magic of aquaponics lies in the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants, creating a closed relationship system.
1. Fish Tanks
– Fish, often species like tilapia, catfish, or trout, are kept in tanks where they produce waste, primarily ammonia. You can check here for the 11 best types of fish to farm.
– Ammonia is harmful to fish but serves as a valuable nutrient for plants.
2. Biological Filtration
– Beneficial bacteria, specifically nitrosomonas, and nitrobacter, convert ammonia into nitrites and then nitrates.
– Nitrates are the nutrient-rich substance that plants eagerly absorb.
3. Grow Beds or Rafts
– Plants are cultivated in grow beds or floating rafts, where their roots dangle in the nutrient-rich water.
– As plants absorb nutrients, they naturally filter and purify the water.
4. Water Circulation
– A pump circulates the cleansed water back into the fish tanks, completing the cycle.
– This continuous loop ensures a balanced ecosystem where both fish and plants grow.
Advantages of Aquaponics
1. Resource Efficiency
– Aquaponics uses 90% less water than traditional soil-based farming, making it an efficient and sustainable option in water-scarce regions.
2. Space Utilization
– Vertical and stacked systems allow for high-density planting, making aquaponics suitable for urban environments and small spaces.
3. Nutrient-Rich Produce
– Plants in aquaponic systems receive a continuous supply of nutrients, resulting in faster growth and more nutritious produce.
4. Reduced Environmental Impact
– The closed relation system minimizes the release of harmful chemicals into the environment, promoting a healthier ecosystem.
5. Diverse Cultivation Possibilities
– Aquaponics supports the growth of various crops, from leafy greens to fruiting plants, providing flexibility for farmers.
5. Fresh, Nutritious, and Organic Produce
– It is easy to produce organic food through aquaponics since there is no fertilizer application. You just need to provide organic feed for your fish and the same organic nutrient will go through the plants’ roots making everything organic.
6. Year-Round Production
– Since this doesn’t depend on rainwater, you can produce food 360 days a year.
7. Cost Saving
– Since there is no need for traditional fertilizer and also uses a small amount of water, it saves a lot of cost after the initial setup.
Disadvantages of Aquaponics
1. Initial Setup Cost
– Establishing an aquaponic system can be expensive due to the need for fish tanks, grow beds, pumps, monitoring equipment, and lighting systems for indoor setups.
2. Technical Knowledge Required
– Successful aquaponics requires an understanding of both aquaculture and hydroponics, making it challenging for beginners without prior experience
3. System Vulnerability
– If one component of the system fails, such as a pump malfunction or fish disease, the entire ecosystem may be at risk.
4. Energy Dependency
– Aquaponics systems may rely on electricity to power pumps and aerators, adding to operational costs and environmental impact.
5. Fish Sensitivity
– Certain fish species are more sensitive to water quality changes, requiring careful monitoring and management.
Factors to consider before aquaponic setups
Before you set up your aquaponic system, you need to consider the following factors to consider as a guide to be successful.
1. Environment
- Light; Since both the plants and fish require light to grow, it could be sunlight or artificial light therefore you need to consider that. When setting up your aquaponics, you need to consider putting up bulbs or a lighting system if your setup is indoors,
- Humidity; the must be moisture in your system so consider evaporation of the place before setting up. This means that you need to consider a place with low temperature
- Water Spillage; you need to ensure that your water tank or pipes are not leaking otherwise there will be water wastage in the system
2. Location
- Water Source; since the fish can’t leave without water, therefore, you need to consider water availability at the site
- Electricity Source; Since there should be submersible pumps pumping water, and also a lighting system, there should be electricity available.
- Ventilation; There should be enough air circulation within the fish tank and plant beds
Conclusion
Aquaponics stands at the intersection of sustainability and innovation, offering a holistic solution to modern agricultural challenges. This closed-loop system, with its intricate balance between fish and plants, showcases a harmonious coexistence that mirrors the delicate equilibrium found in nature. While it presents certain challenges, the numerous advantages of aquaponics make it a compelling choice for individuals and communities seeking a more sustainable and efficient way to produce fresh, nutritious food. As we continue to explore and refine this agricultural method, aquaponics holds the promise of shaping a greener, more sustainable future for food production.


