Fish farming, also known as aquaculture, is hailed as a sustainable solution to meet the ever-growing global demand for seafood. However, beneath the surface of this industry lies a sad reality – cannibalism among farmed fish. In this blog post, we delve deep into the phenomenon of cannibalism in fish farming, the type of fish species where cannibalism is high, exploring its causes, consequences, and potential solutions. So keep reading to the end to learn more about the topic.
What is Fish Cannibalism?
Fish cannibalism in fish farming refers to the situation where fish prey on their own species. In this case, a fish (known as a Predatory Fish) attacks another fish to consume it.
This behavior is prevalent across various species raised in aquaculture settings, including catfish, tilapia, trout, and salmon. Despite its prevalence, the reasons behind cannibalism in fish farming are multifaceted.
One primary cause of cannibalism is the overcrowded conditions in fish farms.
Inadequate or inconsistent feeding practices also increase cannibalism.
Types of fish that have high cannibalism
Cannibalism in fish type varies, so let’s look at some of the common fish that have a high cannibalism rate
Catfish
farming is prevalent in many parts of the world, particularly in regions with abundant freshwater resources. In catfish aquaculture, overcrowding and inadequate feeding practices can trigger cannibalistic behavior among the fish population.
For me, catfish is the number one fish species with the highest cannibalism. They are very violent and attack not only fish but anything that comes their way.
Tilapia
Tilapia is one of the most widely cultivated freshwater fish species globally, prized for its fast growth rate and adaptability to a wide range of environmental conditions.
In overcrowded aquaculture environments, tilapia are known to exhibit cannibalistic behavior, particularly when resources such as food and space are limited
Trout
Trout, including species such as rainbow trout and brown trout, are popular targets for aquaculture due to their delicious flavor and high market demand.
In intensive trout farming operations, overcrowding and competition for resources can lead to aggressive behaviors, including cannibalism.
Salmon
Salmon farming is a significant industry worldwide, supplying a substantial portion of the global seafood market.
In densely stocked salmon farms, cannibalism can occur, particularly among juvenile fish competing for limited space and food resources.
Barramundi
Barramundi, also known as Asian sea bass, is a popular species for aquaculture due to its mild flavor and high nutritional value.
In barramundi farms, cannibalism can occur, especially during the juvenile stage when fish are more vulnerable to aggression and competition.
To check more on types of fish, their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages click HERE
What Are The Stages of Fish’s Life Circle Where Cannibalism Is High?
Fish cannibalism tends to be most prevalent during certain stages of the fish’s life cycle when they are more vulnerable or exhibit certain behaviors that increase the likelihood of aggression and predation.
1. Juvenile Stage
– During the early stages of development, juvenile fish are often more susceptible to cannibalistic behavior due to their small size and limited ability to defend themselves.
2. Fry Stage
– Fry, or newly hatched fish larvae, are extremely vulnerable to predation and cannibalism, especially in species with large clutch sizes where competition for resources is high.
– In hatcheries or nursery facilities, where fry are often reared in confined spaces, cannibalism can occur if adequate precautions are not taken to prevent aggression and provide suitable feeding and shelter options.
3. Weaning Stage
As the fish transition from larval or fry stages to juvenile stages and begin to consume solid food, cannibalism can become more pronounced, particularly if there are disparities in growth rates within the population.
4. Post-stocking Stress Period
– After fish are transferred from hatcheries or nurseries to grow-out ponds or cages, they may experience stress due to environmental changes, transportation, or handling, making them more susceptible to cannibalistic behavior.
– The post-stocking period is critical for acclimating fish to their new surroundings and minimizing stressors that could trigger aggressive behaviors, including overcrowding and competition for resources.
Factors Contributing to Cannibalism
1. Overcrowding in Fish Farms
Overcrowding is a significant issue in intensive fish farming operations. High stocking densities not only intensify competition for resources but also create stressful environments for fish. In such conditions, cannibalism becomes a survival strategy for dominant individuals seeking to assert their dominance and secure access to limited resources.
2. Inadequate Feeding Practices
Proper nutrition is essential for the health and well-being of farmed fish. However, inconsistent feeding schedules or low-quality feed can lead to malnutrition and hunger-induced aggression among fish populations. Or even inadequate feed In some cases, fish may resort to cannibalism as a means of satisfying their hunger when food is scarce.
3. Lack of Environmental Enrichment
Enriching the aquatic environment within fish farms is crucial for promoting natural behaviors and reducing stress among farmed fish. However, many aquaculture facilities lack adequate environmental enrichment, such as hiding places, structures, or natural vegetation. Without these stimuli, fish may exhibit abnormal behaviors, including cannibalism, as a response to environmental stressors.
What Are The Effects of Cannibalism in Fish Farms?
1. Stunted Growth and Poor Health
Cannibalism can have detrimental effects on the growth and development of farmed fish. When larger individuals prey on smaller ones, it results in uneven growth rates within the population. This uneven growth not only reduces the overall productivity of the fish farm but also compromises the quality of the harvested fish.
2. Increased Stress Levels
Cannibalism contributes to elevated stress levels among farmed fish, which can weaken their immune systems and make them more susceptible to diseases. Chronic stress not only impairs fish health but also diminishes their reproductive capabilities, leading to reduced breeding success and offspring viability.
3. Economic Losses for Farmers
From a financial perspective, cannibalism represents a significant loss for fish farmers. Not only does it reduce the overall yield and market value of the harvested fish, but it also increases production costs associated with mitigating the effects of cannibalism and managing its consequences.

4. Fish Mortality
Cannibalism increases fish mortality rate in farms. In fact, I can vehemently say that cannibalism has caused more than half of the fish mortality on my catfish farm. That is why I believe that catfish have the highest cannibalism rate among other species of fish.
What you should know is that, is not only the attacked fish that die as a result of the cannibalism, sometimes even the predatory fish swallow the dominant ones and also die as a result of the bones or the fish itself stuck the throat.
Sometimes they even pick and swallow any external object that finds its way into the pond and that sometimes kills them.

5. Injury to the Farmer
Sometimes the fish also attack any external object that enters the water (this is very common in Pond Aquaculture). This can be said to be self-defense or sometimes they test to see whether is something they can feed on. So in a situation where the farmer puts his hand in the water to check something, for instance oxygen pump, these fish attacks sometimes cause injuries to the person. I have had such encounters several times.
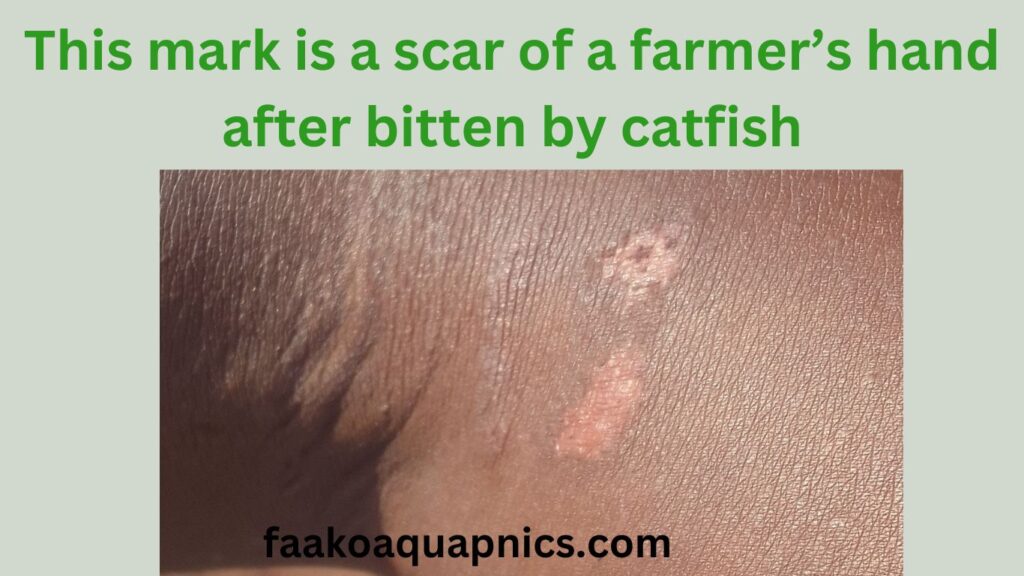
A fish farmer’s hand was injured by fish due to cannibalism
How Prevent Cannibalism in Fish Farming
There is always a way out of every misfortune in life, which includes fish farming. When you implement the listed strategies, if you are not able to prevent cannibalism from occurring on your farm, you will drastically reduce it to the minimum level.
1. Improving Feeding Strategies
One approach to mitigating cannibalism in fish farming is to optimize feeding strategies. Implementing regular feeding schedules and ensuring adequate nutrition can help satisfy the dietary needs of farmed fish, reducing the likelihood of cannibalistic behaviors.
The number of times to feed your fish depends on the age/size of the fish. At the juvenile stage, you may feed them 3 times daily. And when they reach 3 months and above, you can feed them morning and evening alone. And this can continue till you harvest depending on how long or size you want your fish. You may also feed your fish once a day after they reach 4 months and above.
Always make sure you feed your fish when the weather is not too hot or too cool within the day.
Make sure to use the responsive feeding method to feed your fish by observing how they respond to the feed while you feed them.
2. Reducing Stocking Densities
To alleviate overcrowding and minimize competition among fish, farmers can consider reducing stocking densities within their aquaculture facilities. By providing more space and resources per individual fish, farmers can create a less stressful environment that discourages cannibalism.
3. Fish Sorting
One of the most effective ways of handling cannibalism is Fish Sorting. Fish Sorting is the process of selecting fish of similar sizes, colors, weights, and other characteristics for the same pond. In this way, almost all the fish are alike which will reduce cannibalism drastically.
You may check this post for detailed information on how to sort your fish to maximize your profit.

This is one of the reasons you should sort your fish
4. Implementing Environmental Enrichment Strategies
Introducing environmental enrichment measures such as adding shelters, vegetation, or substrate can promote natural behaviors and alleviate stress among farmed fish. These enhancements create a more stimulating and dynamic environment, reducing the incidence of cannibalism and improving overall fish welfare.
5. Introduction of Antibiotics into Fish Pond
Regular check and introduce antibiotics into the fish pond which will go a long way to reduce cannibalism. This can be done either locally way or medicated way. For the local way, you can once in a while add salt to their pond or add bitter leaves to it. But for medically, you need to get the right medicated antibiotics for the pond.
To learn more about how to use salt to treat your fish and reduce cannibalism simply check out this post here.
6. Feeding Non-Carnivorous Diets
One innovative approach to reducing cannibalism in fish farming is to transition towards feeding non-carnivorous diets. By utilizing plant-based or alternative protein sources in fish feed formulations, farmers can minimize the reliance on fishmeal and fish oil derived from wild-caught fish, thereby reducing the pressure on marine ecosystems and mitigating cannibalism.
7. Selective Breeding for Cannibalism Resistance
Selective breeding programs aimed at breeding fish with reduced aggressive tendencies and increased tolerance to crowding can help mitigate cannibalism in aquaculture. By selectively breeding for desirable traits such as docility and social compatibility, farmers can produce fish populations that are less prone to cannibalistic behaviors.
8. Integration of Biological Controls
Integrating biological controls such as predator fish or cleaner fish into aquaculture systems can help regulate population dynamics and reduce the incidence of cannibalism. These natural predators can effectively control the population size of farmed fish and discourage cannibalistic behaviors, thereby promoting a more balanced and sustainable ecosystem within fish farms.
Ethical Considerations and Industry Regulations
1. Addressing Animal Welfare Concerns
As awareness of animal welfare issues continues to grow, there is increasing scrutiny on the ethical implications of cannibalism in fish farming. Addressing these concerns requires a commitment to improving husbandry practices, implementing humane slaughter methods, and prioritizing the welfare of farmed fish throughout their lifecycle
2. Regulatory Frameworks and Guidelines
Government agencies and industry organizations play a vital role in regulating and overseeing the practices of the aquaculture industry. Implementing and enforcing robust regulatory frameworks and industry standards can help ensure compliance with ethical, environmental, and animal welfare considerations, thereby promoting responsible and sustainable fish farming practices.
Every country has its rules and regulations so always try to obey them and even including international laws. In as much as we produce our food, we must also keep the environment in good shape hence the reason for those rules and regulations.
Conclusion
Cannibalism in fish farming is a complex and multifaceted issue that poses significant challenges for the aquaculture industry. However, by understanding the underlying causes, implementing effective mitigation strategies, and embracing sustainable alternatives and innovations, we can work towards building a more ethical, humane, and environmentally sustainable future for fish farming. Through collaborative efforts and collective action, we can strive to mitigate the impacts of cannibalism and foster a more compassionate relationship between humans and the aquatic animals we rely on for sustenance.
Please leave comment in the comment box below





